Ventilation is not just air blowing in through an open window and it certainly isn’t the bathroom fan turned on to get rid of a bad smell.
In a previous blog, I stated that many older houses are now much tighter than the owners believe. Remodeling, changing surfaces and even a coat of paint can do a lot towards tightening the house and reducing its ability to breath. You should, if you own a house that has new siding, exterior windows or doors installed, be concerned that there is an inadequate amount of ventilation. High humidity levels can cause all sorts of visible and concealed moisture damage to a home. Some clues are frost buildup on windows, ice dams, mold and wood decay.
Ventilation, broadly, is an equal exchange of stale air being continually exhausted from the house shell while being replaced by clean atmospheric air at code specified rates.
There are two general methods of ventilation:
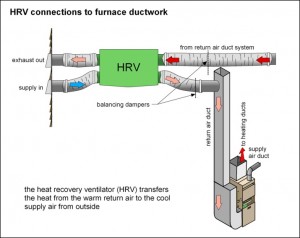
- The first is balanced ventilation. This requires design by an expert in the field. In balanced ventilation two fans of equal volume will be installed. One will suck air into the housing shell from outside and the other will blow stale air from inside the shell to the outside. Often the two air streams pass, side-by-side, through a heat sink material so that the heat being exhausted from the house may be captured and returned in the incoming air. Systems that employ this kind of heat exchange are usually about 70% efficient.
- The other method is unbalanced ventilation. Unbalanced ventilation can be a fan sucking air into the house from outside and exhausting, by the pressure created, through an existing vent. Or, more typically, it would be just the opposite. Outside air would come in to the house through a lowering of pressure caused by an existing exhaust fan operating in the home. This method is not nearly as efficient as balanced ventilation but it will do the job.
The easiest and most economical way to ventilate your home is unbalanced ventilation. This is something that you can do yourself at a cost of a few hundred dollars. Some homes may already have the equipment in place and it will take little effort to implement. First you will need to select an existing exhaust fan in the bathroom or perhaps in the kitchen that is vented to the outside. 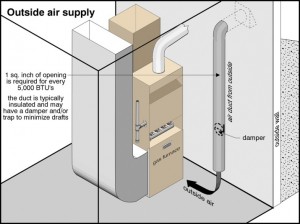 Next, you need to create a vent opening in the basement, connect an insulated flexible air duct, and extend this pipe to the floor. The outside vent cover will need a screen to prevent vermin from entering the home. You may already have this pipe; it would be an open pipe near the furnace called an outside air supply. Finally, turn on the exhaust fan and run continuously. This will remove the stale warm moist damaging air in the home , replace it with fresh cold dry outside air and not depressurize the home. You are now controlling the quality and moisture level of the indoor air.
Next, you need to create a vent opening in the basement, connect an insulated flexible air duct, and extend this pipe to the floor. The outside vent cover will need a screen to prevent vermin from entering the home. You may already have this pipe; it would be an open pipe near the furnace called an outside air supply. Finally, turn on the exhaust fan and run continuously. This will remove the stale warm moist damaging air in the home , replace it with fresh cold dry outside air and not depressurize the home. You are now controlling the quality and moisture level of the indoor air.
Any exhaust fan in the home will give you a result. Just remember that the smallest fan required by code is 40 CFM. The higher the CFM fan rating the quicker the home will complete a complete air change. Fans are typically rated from 40 to 130 CFM.
Doug Hastings
MN Home Inspector, Minneapolis & St. Paul
ASHI certified inspector, ACI
Kaplan University, Home Inspection Lead Instructor
Rob ‘Pops’ Leslie
Kaplan Professionals, Retired